Gantries are an essential component for ion therapy facilities, and are what allow the beam of ions to be directed precisely towards the patient's tumor from different angles.
A size and cost reduction of gantries is primarily achievable through the use of superconductivity. The NIMMS project is therefore in collaboration with the HITRIplus EU Project, in which their is a focus on developing an optimized beam optics design for a superconducting gantry design. This collaboration, referred to as HITRIplus Task 7.3, includes partners such as CERN, CNAO, SEEIIST, and Riga Technical University.
The HITRIplus* collaboration has examined four different mechanical structures to support the magnet arrangement. After considering factors such as energy consumption during operation, safety against unexpected breakages, and positioning precision, the was a clear preference for a balanced structure with a counterweight. The four structural options were: balanced SIGRUM design, simple-supported design, side and cradle supported with a rotation capability of 210 degrees, and a full-turn structure allowing for a 360-degree rotation.
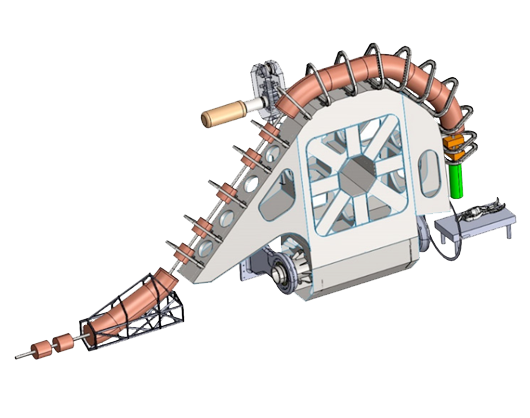
EuroSIG
EuroSig, previously named SIGRUM, is an innovative carbon ion gantry design. By utilizing lightweight superconducting magnets, the gantry design can be at least half as light, compared to current normal conducting magnet gantries.
 |
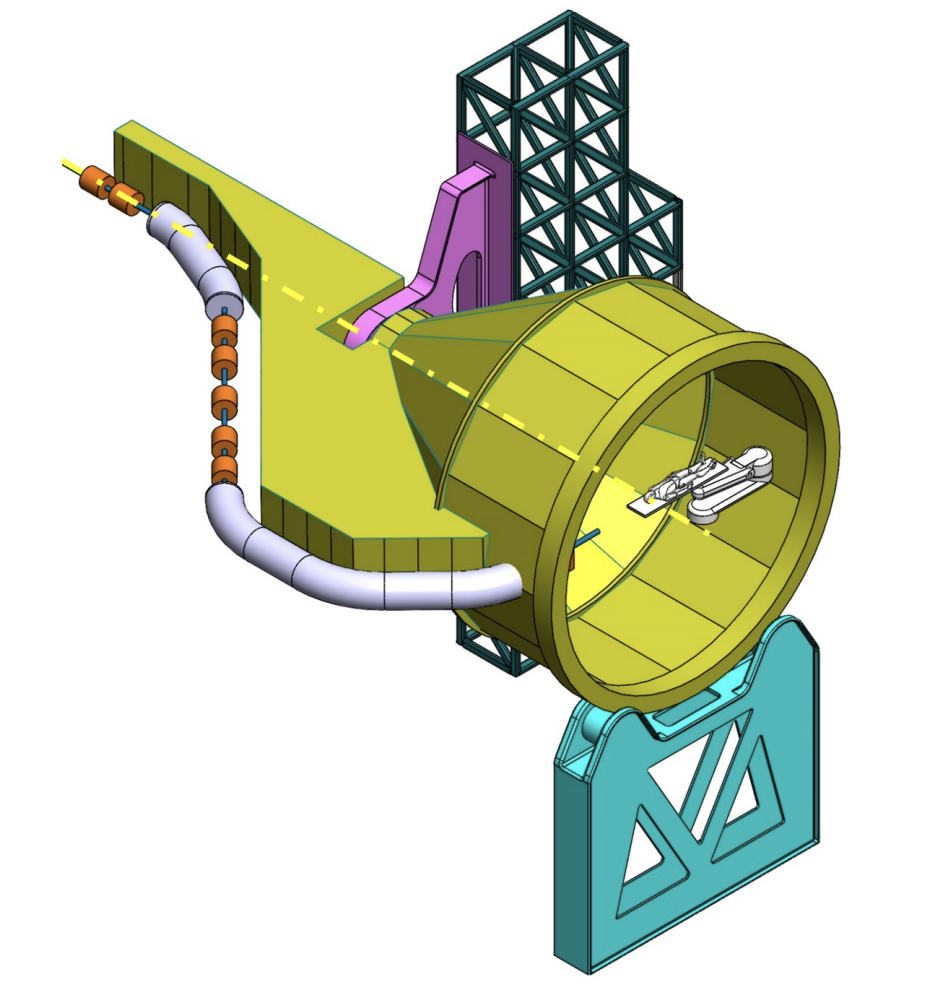
GaToroid
GaToroid is a novel configuration of a beam delivery system for charged particles therapy based on a steady-state, axis-symmetric field configuration. The basic idea is to use fixed toroidal magnets, producing an axis-symmetric (or periodical axis-symmetric) field configuration that can bend beams from several directions onto the patient location. In principle, neither magnets nor patient need to be moved. In addition, the field of the magnets of this toroidal gantry is static. Such system is perfectly adapted to FLASH therapy, a novel method of beam dose delivery that has shown benefits for electrons and potential for hadrons.
More recently a “compact GaToroid” is in study, suitable for 200 MeV electron beams (VHEE), and protons at 70 MeV, which with high delivery dose rates, can take advantage of the FLASH effect. Learn more about this initiative below.
Innovative superconducting gantries will be the forefront of the solutions towards making heavy ion therapy more accessible to a wider array of medical institutions.

